7 Types Of Generative AI: Explained With Examples
Key Takeaways
- Understand the types of generative AI and their use cases.
- Learn how each model works and solves unique problems.
- Identify practical benefits across industries and workflows.
- See real examples of generative AI types in action.
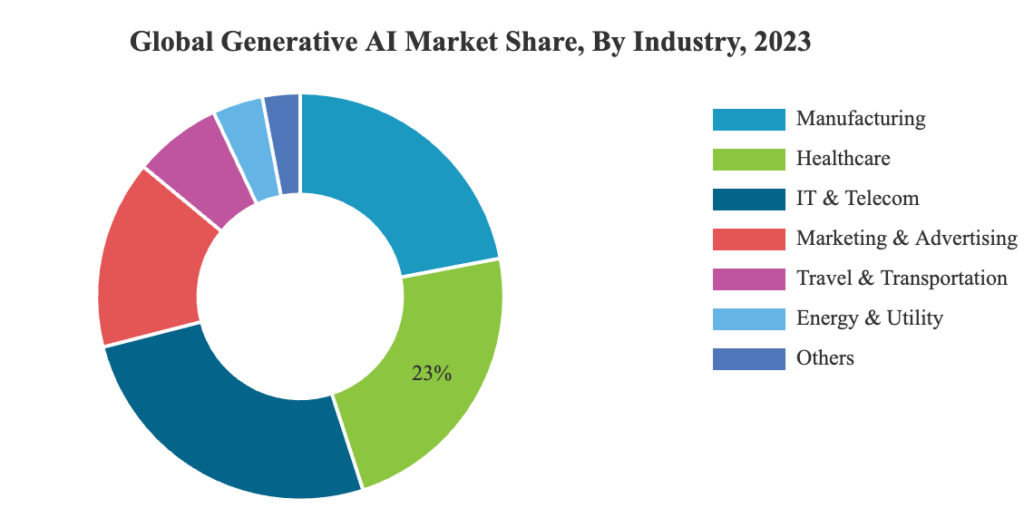
You hear about generative AI everywhere. It is in the news, on social media, and even in everyday conversations. Generative AI demand is projected to rise by 42% annually as adoption accelerates (Bloomberg).
But here is the problem: while interest is exploding, clarity is not.
Most explanations are either too technical (think whitepapers on arXiv) or too vague (like the fluffy ‘AI is the future’ posts flooding LinkedIn). They sound like they are written for AI scientists, not for business owners, product managers, or curious learners. You want to understand the real differences between models, when to use each one, and why it matters for your goals.
This article breaks down the different types of generative AI. I will walk you through each model, share examples from real projects, and point out where they shine. You will also see how businesses from healthcare to fintech are already using them.
When exploring the different types of generative AI, it’s useful to consider how generative AI technologies work to generate text, images, audio, and more from learned patterns.
What are generative AI models?
A generative AI model is a form of machine learning that does more than process data, it creates it. By studying huge sets of examples, these models learn patterns in language, visuals, sound, and more. Then, they use that knowledge to produce new content that mirrors the style and structure of what they have learned.
Businesses today are increasingly exploring these capabilities. Often, with the support of an artificial intelligence app development company like Tech Exactly, you can build smarter, future-ready solutions.
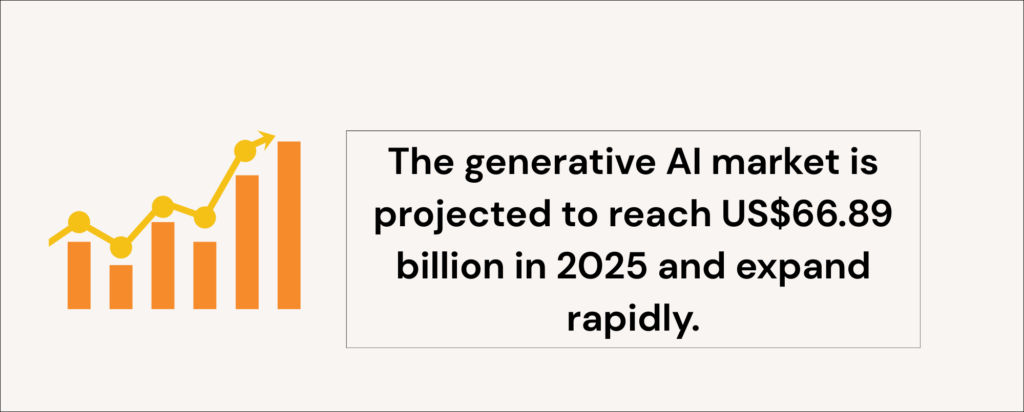
A report by Statista predicts that generative AI will reach US$66.89 bn in 2025. The key difference from traditional AI? Instead of just analysing and making decisions, generative AI focuses on originality. It can design lifelike images, draft engaging articles, compose music, or even simulate voices.
With so many types of generative AI models, each suited to specific tasks, choosing the right one means better results and safer handling of sensitive information. Thus, understanding generative AI categories and how they work is essential before building solutions.
7 Main Types of Generative AI
Generative AI comes in many forms, each designed to create new data that looks and feels like real-world examples. While the approaches differ, they all share the ability to learn from large datasets and produce original outputs. Below are the generative AI models, what they do, and how they are applied in real scenarios.
1. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
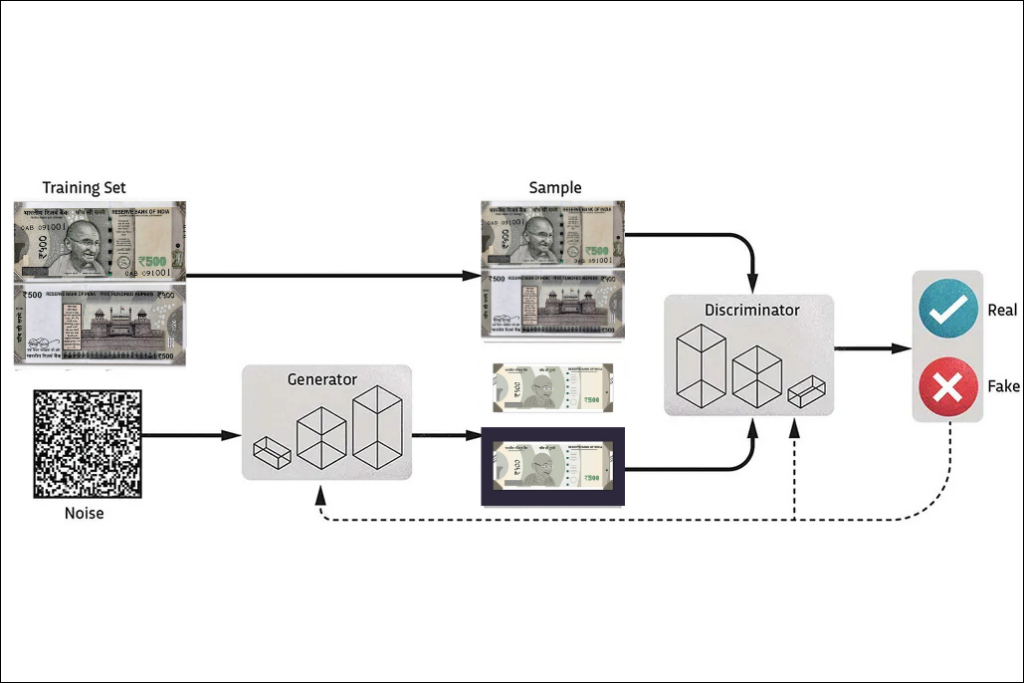
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) are one of the most recognized types of generative AI models, consisting of two core components: a generator and a discriminator. Together, they refine each other’s performance through adversarial training.
- Generator: Produces new data samples based on the patterns learned from the training dataset.
- Discriminator: Evaluates whether each output is “real” (matching the training data distribution) or “fake” (deviating from the distribution), then sends feedback to the generator to help it improve.
This interplay allows GANs to generate content that is visually and statistically almost indistinguishable from real-world data.
Here’s a scenario: a counterfeiter trying to make fake money (generator) and a police officer trying to catch fakes (discriminator). Over time, the counterfeiter gets better at making realistic bills, and the officer gets sharper at spotting flaws until the fakes become nearly indistinguishable.
Use cases:
- Financial services: Generating synthetic transaction datasets to train fraud detection models without exposing sensitive information.
- Public sector: Creating synthetic population datasets for policy modelling without sharing personal data.
- Manufacturing: Producing realistic virtual prototypes to speed up product design and stress testing. To know more, read our blog on how GenAI is empowering production in the manufacturing industry.
To explain it briefly, here’s an example in Healthcare
A hospital wants to improve the accuracy of its lung cancer detection system. However, it only has a limited number of high-quality CT scans. Using GANs, data scientists can generate realistic synthetic CT images of lungs with and without tumours. These images are then added to the training set of the diagnostic AI model. As a result, the model becomes more accurate at identifying early signs of cancer, without risking patient privacy or relying solely on scarce real-world scans.
As per National Library of Medicine, in Italy, conditional GANs were used to create synthetic datasets of cancer patients from telemedicine consultations. These data helped build models predicting patient needs (e.g., frequency of remote visits), achieving prediction accuracy around 0.8.
2. Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
Variational autoencoders (VAEs) are generative AI types that focus on learning efficient latent representations of data. They encode input data into a compressed “latent space” and then decode it back to reconstruct similar but not identical examples, introducing controlled variation.
- Encoder: Compresses the input data into a probabilistic latent space representation.
- Decoder: Reconstructs new data points from this latent representation.
Think of a recipe book. Instead of copying every dish exactly, you write down the key ingredients and steps (compressed version). Later, when you cook, you might vary the spices or portions a little, so each meal is slightly different but still tastes like the original dish.
Use cases:
- Security: Simulating rare cyberattack scenarios to train detection systems on unseen threats.
- Language and media: Generating variations of written or spoken content for multilingual applications.
- Manufacturing: Designing multiple feasible variants of a product before physical prototyping.
3. Autoregressive Models
Autoregressive models generate sequences by predicting the next element based on previous ones. This makes them highly effective for text, music, and time-series generation.
They learn the conditional probability of each next step in the sequence, enabling them to produce coherent, context-aware outputs. One best examples is ChatGPT.
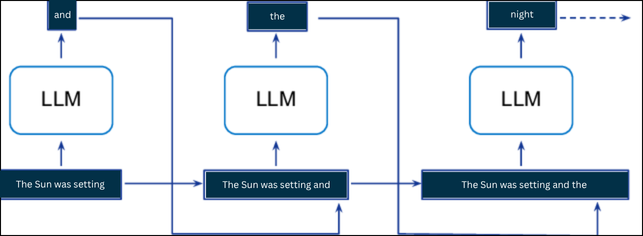
How Autoregressive Models Work
a. These models create data one piece at a time, not all at once.
b. Based on context, each new word or token depends on what came before. For example, from “I like”, the model may predict “coffee”.
c. ChatGPT Example
If you write “The sun was setting…”. The model might add “and”. With the new sequence “The sun was setting and”, it may predict “the”. This continues, word by word, until a full sentence is formed.
Use cases:
- Language models: Generating human-like written or spoken content, such as chatbots( Siri and Alexa) or translation tools.
- Finance: Predicting market trends by generating plausible future price sequences for risk analysis.
Example: Suppose a trading firm wants to analyse how a stock might behave over the next 30 days.
- They feed the model historical stock prices (say, the last 3 years).
- The autoregressive model learns patterns such as daily fluctuations, seasonal cycles, and reactions to economic events.
- Starting from the latest closing price, the model generates the next day’s plausible price.
- That predicted value is then fed back in to generate the price for the following day, continuing step by step until a full 30-day sequence is built.
- The firm runs this simulation thousands of times, producing a range of possible futures instead of one rigid forecast.
Why it matters: Analysts can see scenarios like steady growth, sharp dips, or sudden rallies and then stress-test portfolios against each case to reduce risk exposure.
- Security and compliance: Creating simulated phishing messages for employee training on recognizing threats.
- Entertainment: Composing original music or generating scripts for creative media.
| Industry | Rate of Generative AI Adoption |
| Marketing and Advertising | 37% |
| Technology | 35% |
| Consulting | 30% |
| Teaching | 19% |
| Accounting | 16% |
| Healthcare | 15% |
Source: Demandsage
4. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) are an earlier but still valuable category in the generative AI models list, designed to handle sequential data with temporal dependencies. They maintain a “memory” of previous inputs, making them suitable for tasks where context is crucial.
Use cases:
- Language: Generating coherent paragraphs or speech by remembering earlier parts of the conversation.
- Content generation: Writing poetry or stories that maintain thematic consistency.
- Security: Analyzing and simulating network traffic patterns to detect anomalies.
Example of RNNs in the Energy Sector
A German energy provider used RNNs to predict how much electricity people would need at different times of the day. By learning from past data like usage patterns and weather, the system helped them balance supply and demand more efficiently. This made grid management smoother and reduced the risk of power shortages. (Source)
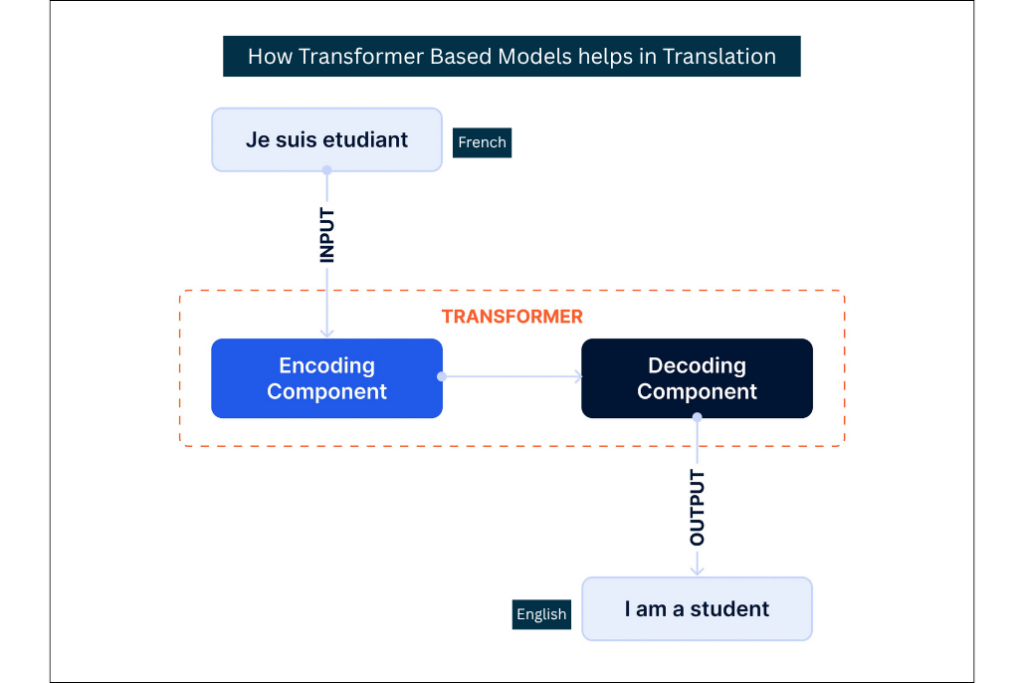
5. Transformer-based Models
Say you are reading a book. When you come across a character’s name in chapter 10, you instantly recall their first appearance back in chapter 2. You do not need to reread every page in between. You simply focus attention on the important parts that give meaning.
Transformers work the same way. Transformer-based architectures have become one of the most dominant generative AI categories. Instead of processing text word by word like RNNs, they use an attention mechanism to decide which parts of the input matter most at any point. This allows them to quickly connect information across long passages and generate accurate, context-aware outputs.
Use cases:
- Language and communication: Powering advanced AI chatbots, translation systems, and summarization tools.
Tech Exactly worked with a US-based self-development platform that offers online quizzes for personal development, transformational resources embedded with a GenAI-powered chatbot. As a result of real-time personalized support on the platform, it helped drive 100,000+ engaged members with 600,000+ quizzes taken by its members.
- Security: Detecting sensitive information in large-scale text datasets before public distribution.
- Learning platforms: Generating personalized educational content in intelligent tutoring systems.
- Media: Creating long-form, coherent narratives for film, games, or marketing campaigns.
6. Reinforcement Learning for Generative Tasks
In this generative AI type, reinforcement learning (RL) is used to improve a generative model by rewarding desirable outcomes and penalizing poor ones. Instead of relying solely on training data, RL enables the model to learn through trial and error to meet specific goals.
Let’s say you are training a pet to perform tricks. Each time the pet does the trick correctly, you give it a treat (reward). If it does something wrong, you withhold the treat (penalty). Over time, it learns which actions earn rewards and repeats them more often.
Use cases:
- Security training: Simulating complex cyberattack strategies to harden defence systems.
- Robotics: Designing efficient motion sequences for autonomous machines.
- Finance: Generating trading strategies optimized for long-term returns under changing market conditions. To learn more about the use cases of Generative AI in Fintech, read this blog.
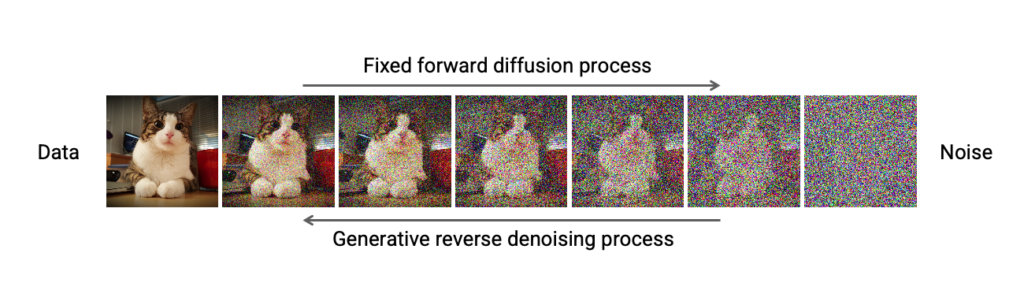
7. Diffusion models
Diffusion models are one of the newer types of generative models. Imagine you have a clear photograph. You start sprinkling tiny dots of “static” (like TV noise) on it until it becomes completely unrecognizable. A diffusion model learns the reverse process: how to carefully remove the noise step by step until the picture reappears.
Now, instead of starting with a real photo, the model begins with pure noise and gradually clears it away, but this time it uncovers a new image it has learned to create, like a realistic face, landscape, or artwork that never existed before.
Use cases:
- Media and marketing: Generating photorealistic images using DALL-E or Stable Diffusion for campaigns without relying on stock photography.
After using UX Pilot, our VP of Design shares how generative AI has become an integral part of their workflow:
– AI helps answer questions, suggests creative directions, and aids in decision-making based on user personas.
– It provides a platform that reduces the need to design everything from scratch.
– AI generates visuals that align closely with design requirements, saving time and improving accuracy.
- Healthcare: Creating synthetic but realistic medical scans for AI training without compromising sensitive data.
- Manufacturing: Visualizing product concepts at different design stages before production.
- Security: Testing visual recognition systems against highly realistic synthetic images to ensure robustness.
Main Benefits Of Generative AI Models
When we look at the different types of Gen-AI, it is easy to see why they have become so popular. No matter which category you pick from the generative AI models list – GANs, VAEs, transformers, or diffusion models- they all bring unique strengths. At the core, the main benefits of generative models make complex tasks easier, smarter, and more secure, while opening doors to new possibilities.
Driving innovation
Gen-AI models allow businesses to test new ideas quickly. For example, creating prototypes, simulating real-world scenarios, or generating content for marketing. All these can be done without even starting from scratch.
👉 Read our blog “Benefits of AI Development Service for Mobile Apps” to understand how Gen AI can translate strategies into real business growth.
Simplifying routine work
Many repetitive jobs like writing drafts, analyzing distribution data, or enhancing images are handled by generative AI models. This saves time, reduces human error, and keeps workflows efficient.
With a Gen AI tool like Windsurf, our tech team has been able to deliver projects faster and more cost-effectively. The AI reduces turnaround times, improves quality, and enhances collaboration. This directly impacts our client satisfaction and delivery timelines.
Providing tailored experiences
By learning from sensitive information like user behaviour or language preferences, different types of Gen-AI can deliver highly personalized recommendations in industries like healthcare, finance, or e-commerce.
Here’s a work-in-progress fintech project of Tech Exactly.
The client came to us stating that borrowers often struggle to get quick, accurate answers about their loan terms. Whether it is repayment dates, interest clauses, or due amounts. Traditional support teams spend a lot of time manually searching contracts, which slows down response times and increases costs.
To solve this, we are building a Gen-AI-powered loan servicing agent that makes borrower interactions seamless.
Here is how GenAI fits in:
- Natural Language Understanding (NLP): The voice agent listens to borrower questions.
- Contract Parsing (automation): A rules-based parser identifies the right section of the contract.
- Generative AI (the key role): GenAI then takes that raw clause or data and rewrites it into a clear, conversational response, something a borrower can instantly understand.
- Voice Delivery: Using ElevenLabs, the response is spoken back to the borrower in real time.
👉 Instead of confusing legal text, borrowers hear “Your next EMI is due on 12th September, with no late fee if paid before the 15th”. This tailored experience reduces support load and ensures quick, personalized support.
Aiding problem-solving
Generative AI categories excel at breaking down complex problems. Like predicting energy demands, generating medical images for diagnostics, they help experts make better decisions while maintaining data security.
Domain expertise
After reading the 7 types of gen-AI models list, you will agree that each type is specialized for certain tasks. Transformers are great with language, autoregressive models excel in content generation, and diffusion models are powerful for creating high-quality visuals. This domain focus ensures better outcomes across industries.
Final Thought
When you step back and look at Gen-AI, one thing becomes clear: they are more than tools for generating content. They act more like catalysts for transformation. Whether you are exploring the many generative AI types for innovation, security, or smarter distribution of resources, these models have become essential across industries.
Understanding the Gen-AI models list and their use cases helps organizations adopt the right approach, making the future of work more efficient, creative, and secure.
At Tech Exactly, we specialize as a generative AI development company, helping businesses make the most of the different types of generative models to create secure, scalable, and future-ready solutions.
If you are looking to explore the potential of generative AI, our experts can guide you in choosing the right approach. Feel free to write to us at info@techexactly.com
FAQ
The seven main types are GANs, VAEs, autoregressive models, RNNs, transformers, reinforcement learning for generative tasks, and diffusion models.
Transformer-based models and autoregressive models are most effective for generating human-like text.
Traditional AI analyses data and makes predictions, while generative AI creates new data such as text, images, audio, or simulations.
Yes, when applied responsibly with the right data governance and compliance, generative AI can generate value without compromising security.
Healthcare, finance, marketing, manufacturing, and education are leading adopters, each using generative AI for tailored innovation and efficiency.
Generative AI models are AI systems that create new content such as text, images, audio, or code by learning patterns from existing data.
Common types include GANs, Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), Transformers, Diffusion models, Autoregressive models, Flow-based models, and Energy-based models.
A Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) uses two neural networks—a generator and a discriminator—to create realistic synthetic data.
To build a generative AI model, choose the right architecture, prepare training data, train the model using frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch, and optimize the output.
Python is the most commonly used language because it supports popular AI frameworks and libraries.
Generative AI models are used for content generation, chatbots, image creation, drug discovery, and software development.
Generative AI models require large datasets such as text, images, or audio depending on the type of model being developed.
Developers commonly use tools like TensorFlow, PyTorch, Hugging Face, and Stable Diffusion.
Pallabi Mahanta, Senior Content Writer at Tech Exactly, has over 5 years of experience in crafting marketing content strategies across FinTech, MedTech, and emerging technologies. She bridges complex ideas with clear, impactful storytelling.